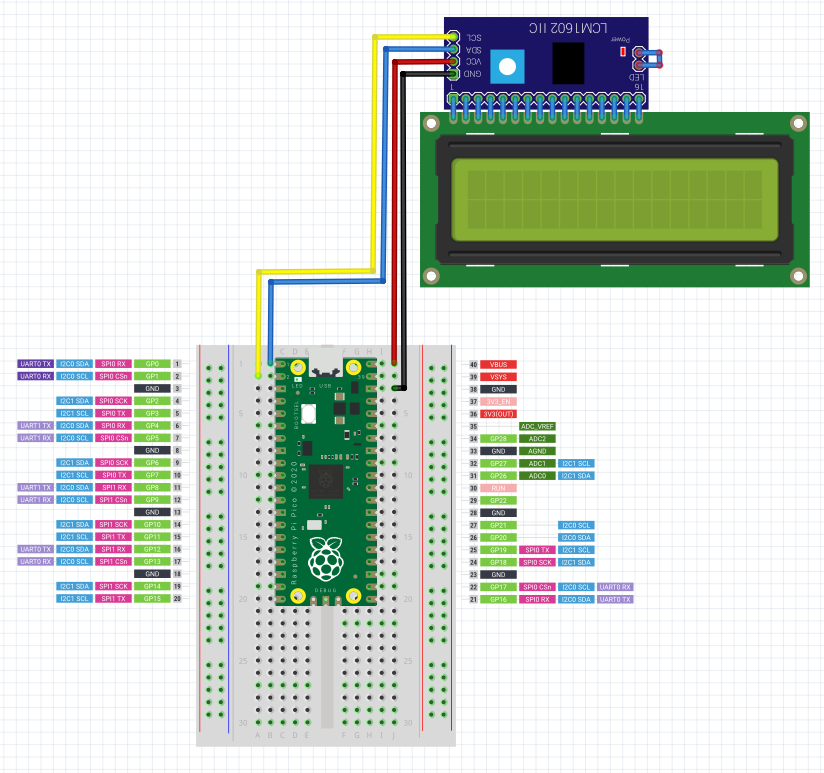
Pi Pico - LCD Module
Code provided by: T-622
lcd_api.py
import time class LcdApi: # Implements the API for talking with HD44780 compatible character LCDs. # This class only knows what commands to send to the LCD, and not how to get # them to the LCD. # # It is expected that a derived class will implement the hal_xxx functions. # # The following constant names were lifted from the avrlib lcd.h header file, # with bit numbers changed to bit masks. # HD44780 LCD controller command set LCD_CLR = 0x01 # DB0: clear display LCD_HOME = 0x02 # DB1: return to home position LCD_ENTRY_MODE = 0x04 # DB2: set entry mode LCD_ENTRY_INC = 0x02 # DB1: increment LCD_ENTRY_SHIFT = 0x01 # DB0: shift LCD_ON_CTRL = 0x08 # DB3: turn lcd/cursor on LCD_ON_DISPLAY = 0x04 # DB2: turn display on LCD_ON_CURSOR = 0x02 # DB1: turn cursor on LCD_ON_BLINK = 0x01 # DB0: blinking cursor LCD_MOVE = 0x10 # DB4: move cursor/display LCD_MOVE_DISP = 0x08 # DB3: move display (0-> move cursor) LCD_MOVE_RIGHT = 0x04 # DB2: move right (0-> left) LCD_FUNCTION = 0x20 # DB5: function set LCD_FUNCTION_8BIT = 0x10 # DB4: set 8BIT mode (0->4BIT mode) LCD_FUNCTION_2LINES = 0x08 # DB3: two lines (0->one line) LCD_FUNCTION_10DOTS = 0x04 # DB2: 5x10 font (0->5x7 font) LCD_FUNCTION_RESET = 0x30 # See "Initializing by Instruction" section LCD_CGRAM = 0x40 # DB6: set CG RAM address LCD_DDRAM = 0x80 # DB7: set DD RAM address LCD_RS_CMD = 0 LCD_RS_DATA = 1 LCD_RW_WRITE = 0 LCD_RW_READ = 1 def __init__(self, num_lines, num_columns): self.num_lines = num_lines if self.num_lines > 4: self.num_lines = 4 self.num_columns = num_columns if self.num_columns > 40: self.num_columns = 40 self.cursor_x = 0 self.cursor_y = 0 self.implied_newline = False self.backlight = True self.display_off() self.backlight_on() self.clear() self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ENTRY_MODE | self.LCD_ENTRY_INC) self.hide_cursor() self.display_on() def clear(self): # Clears the LCD display and moves the cursor to the top left corner self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_CLR) self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_HOME) self.cursor_x = 0 self.cursor_y = 0 def show_cursor(self): # Causes the cursor to be made visible self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY | self.LCD_ON_CURSOR) def hide_cursor(self): # Causes the cursor to be hidden self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY) def blink_cursor_on(self): # Turns on the cursor, and makes it blink self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY | self.LCD_ON_CURSOR | self.LCD_ON_BLINK) def blink_cursor_off(self): # Turns on the cursor, and makes it no blink (i.e. be solid) self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY | self.LCD_ON_CURSOR) def display_on(self): # Turns on (i.e. unblanks) the LCD self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL | self.LCD_ON_DISPLAY) def display_off(self): # Turns off (i.e. blanks) the LCD self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_ON_CTRL) def backlight_on(self): # Turns the backlight on. # This isn't really an LCD command, but some modules have backlight # controls, so this allows the hal to pass through the command. self.backlight = True self.hal_backlight_on() def backlight_off(self): # Turns the backlight off. # This isn't really an LCD command, but some modules have backlight # controls, so this allows the hal to pass through the command. self.backlight = False self.hal_backlight_off() def move_to(self, cursor_x, cursor_y): # Moves the cursor position to the indicated position. The cursor # position is zero based (i.e. cursor_x == 0 indicates first column). self.cursor_x = cursor_x self.cursor_y = cursor_y addr = cursor_x & 0x3f if cursor_y & 1: addr += 0x40 # Lines 1 & 3 add 0x40 if cursor_y & 2: # Lines 2 & 3 add number of columns addr += self.num_columns self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_DDRAM | addr) def putchar(self, char): # Writes the indicated character to the LCD at the current cursor # position, and advances the cursor by one position. if char == '\n': if self.implied_newline: # self.implied_newline means we advanced due to a wraparound, # so if we get a newline right after that we ignore it. pass else: self.cursor_x = self.num_columns else: self.hal_write_data(ord(char)) self.cursor_x += 1 if self.cursor_x >= self.num_columns: self.cursor_x = 0 self.cursor_y += 1 self.implied_newline = (char != '\n') if self.cursor_y >= self.num_lines: self.cursor_y = 0 self.move_to(self.cursor_x, self.cursor_y) def putstr(self, string): # Write the indicated string to the LCD at the current cursor # position and advances the cursor position appropriately. for char in string: self.putchar(char) def custom_char(self, location, charmap): # Write a character to one of the 8 CGRAM locations, available # as chr(0) through chr(7). location &= 0x7 self.hal_write_command(self.LCD_CGRAM | (location << 3)) self.hal_sleep_us(40) for i in range(8): self.hal_write_data(charmap[i]) self.hal_sleep_us(40) self.move_to(self.cursor_x, self.cursor_y) def hal_backlight_on(self): # Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight on. # If desired, a derived HAL class will implement this function. pass def hal_backlight_off(self): # Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight off. # If desired, a derived HAL class will implement this function. pass def hal_write_command(self, cmd): # Write a command to the LCD. # It is expected that a derived HAL class will implement this function. raise NotImplementedError def hal_write_data(self, data): # Write data to the LCD. # It is expected that a derived HAL class will implement this function. raise NotImplementedError def hal_sleep_us(self, usecs): # Sleep for some time (given in microseconds) time.sleep_us(usecs)
pico_i2c_lcd.py
import utime import gc from lcd_api import LcdApi from machine import I2C # PCF8574 pin definitions MASK_RS = 0x01 # P0 MASK_RW = 0x02 # P1 MASK_E = 0x04 # P2 SHIFT_BACKLIGHT = 3 # P3 SHIFT_DATA = 4 # P4-P7 class I2cLcd(LcdApi): #Implements a HD44780 character LCD connected via PCF8574 on I2C def __init__(self, i2c, i2c_addr, num_lines, num_columns): self.i2c = i2c self.i2c_addr = i2c_addr self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([0])) utime.sleep_ms(20) # Allow LCD time to powerup # Send reset 3 times self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION_RESET) utime.sleep_ms(5) # Need to delay at least 4.1 msec self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION_RESET) utime.sleep_ms(1) self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION_RESET) utime.sleep_ms(1) # Put LCD into 4-bit mode self.hal_write_init_nibble(self.LCD_FUNCTION) utime.sleep_ms(1) LcdApi.__init__(self, num_lines, num_columns) cmd = self.LCD_FUNCTION if num_lines > 1: cmd |= self.LCD_FUNCTION_2LINES self.hal_write_command(cmd) gc.collect() def hal_write_init_nibble(self, nibble): # Writes an initialization nibble to the LCD. # This particular function is only used during initialization. byte = ((nibble >> 4) & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte | MASK_E])) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte])) gc.collect() def hal_backlight_on(self): # Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight on self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([1 << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT])) gc.collect() def hal_backlight_off(self): #Allows the hal layer to turn the backlight off self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([0])) gc.collect() def hal_write_command(self, cmd): # Write a command to the LCD. Data is latched on the falling edge of E. byte = ((self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | (((cmd >> 4) & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA)) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte | MASK_E])) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte])) byte = ((self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | ((cmd & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA)) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte | MASK_E])) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte])) if cmd <= 3: # The home and clear commands require a worst case delay of 4.1 msec utime.sleep_ms(5) gc.collect() def hal_write_data(self, data): # Write data to the LCD. Data is latched on the falling edge of E. byte = (MASK_RS | (self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | (((data >> 4) & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA)) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte | MASK_E])) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte])) byte = (MASK_RS | (self.backlight << SHIFT_BACKLIGHT) | ((data & 0x0f) << SHIFT_DATA)) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte | MASK_E])) self.i2c.writeto(self.i2c_addr, bytes([byte])) gc.collect()
Find i2c address (optional):
import machine SDA = machine.Pin(0) SCL = machine.Pin(1) i2c = machine.I2C( 0, sda = SDA, scl = SCL, freq = 400000 ) if ( len(i2c.scan()) > 0 ): print( "There are", str(len(i2c.scan())), end='' ) print( " i2c devices attached...") print( "Found i2c device at address: ", i2c.scan(), end='' ) print( " Hex: ", hex(i2c.scan()[0]) ) else: print( "No i2c devices found..." )
Demonstration of all features:
import utime import machine from machine import I2C from lcd_api import LcdApi from pico_i2c_lcd import I2cLcd I2C_ADDR = 0x27 I2C_NUM_ROWS = 2 I2C_NUM_COLS = 16 SDA = machine.Pin(0) SCL = machine.Pin(1) def test_main(): #Test function for verifying basic functionality print("Running test_main") i2c = machine.I2C( 0, sda = SDA, scl = SCL, freq = 400000 ) print("Running 1") lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, I2C_ADDR, I2C_NUM_ROWS, I2C_NUM_COLS) print("Running 2") lcd.putstr("It Works!") utime.sleep(2) lcd.clear() count = 0 while True: lcd.clear() time = utime.localtime() lcd.putstr("{year:>04d}/{month:>02d}/{day:>02d} {HH:>02d}:{MM:>02d}:{SS:>02d}".format( year=time[0], month=time[1], day=time[2], HH=time[3], MM=time[4], SS=time[5])) if count % 10 == 0: print("Turning cursor on") lcd.show_cursor() if count % 10 == 1: print("Turning cursor off") lcd.hide_cursor() if count % 10 == 2: print("Turning blink cursor on") lcd.blink_cursor_on() if count % 10 == 3: print("Turning blink cursor off") lcd.blink_cursor_off() if count % 10 == 4: print("Turning backlight off") lcd.backlight_off() if count % 10 == 5: print("Turning backlight on") lcd.backlight_on() if count % 10 == 6: print("Turning display off") lcd.display_off() if count % 10 == 7: print("Turning display on") lcd.display_on() if count % 10 == 8: print("Filling display") lcd.clear() string = "" for x in range(32, 32+I2C_NUM_ROWS*I2C_NUM_COLS): string += chr(x) lcd.putstr(string) count += 1 utime.sleep(2) #if __name__ == "__main__": test_main()
Simple Example:
from machine import I2C from lcd_api import LcdApi from pico_i2c_lcd import I2cLcd I2C_ADDR = 0x27 I2C_NUM_ROWS = 2 I2C_NUM_COLS = 16 SDA = machine.Pin(0) SCL = machine.Pin(1) i2c = machine.I2C( 0, sda = SDA, scl = SCL, freq = 400000 ) lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, I2C_ADDR, I2C_NUM_ROWS, I2C_NUM_COLS) lcd.putstr("Simple line of text!")